Influenza
Definition
- Acute respiratory disease caused by influenza virus (Influenza virus A/B/C/D) infection
Causative pathogen
- Influenza virus A/B/C/D
Transmission route
- Droplet transmission
Common targets
- Occurs in all age groups
Incubation period and contagious period
- 1 to 4 days (average 2 days)
- From 1 day before the onset of symptoms to 5 to 7 days after onset * However, in children or immunocompromised individuals, the virus shedding period may extend beyond 10 days.
Clinical symptoms
- High fever (38 to 40℃), respiratory symptoms such as dry cough and sore throat, as well as general symptoms like headache, muscle pain, fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite
- Accompanied by runny nose, nasal congestion, eye pain, vomiting, and abdominal pain
Treatment
- Symptomatic treatment
- Antiviral treatment
Prevention
- Vaccination
- Proper handwashing and adherence to cough etiquette
- Avoidance of touching eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands
- During the symptomatic period, limiting visits to workplaces, schools, and public places, and resting at home
Diagnosis/Reporting criteria
- Reporting scope: Patients, suspected cases
- (Patient) A person who shows clinical symptoms consistent with influenza and is confirmed to be infected with the infectious pathogen according to diagnostic criteria
- (Suspected case) A person showing fever above 38℃ along with cough or sore throat
- Diagnostic criteria: Detection of specific genes in the specimen
- Reporting period: Report within 7 days
- Responsible department
- (Reporting) Division of Infectious Disease Control
- (Diagnosis) Division of Emerging Infectious Diseases
Clinical Surveillance of Influenza-like Illness (ILI)
Case definition
- Influenza patient
- A person who shows clinical symptoms consistent with influenza and is confirmed to be infected with the infectious pathogen according to diagnostic criteria
- Influenza-like illness (ILI)
- A person showing fever above 38°C along with cough or sore throat
Objective
- Continuous monitoring of trends in the occurrence of influenza-like illness to identify outbreaks early
- Provision of foundational data for establishing national influenza control measures
Designation of sentinel surveillance sites
- 300 outpatient institutions nationwide (pediatrics, internal medicine, family medicine, otorhinolaryngology)
- Weekly surveillance (status reports of influenza-like illness patients among those treated from Sunday to Saturday within 7 days)
- Influenza sentinel surveillance (clinical) flowchart
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- Designation of sentinel surveillance sites
- Analysis of surveillance data and information feedback
- City/Province
- Confirming and preparing for influenza outbreak situations Distribution of feedback materials, etc.
- Distribution of feedback materials, etc.
- City/County/District Health Center
- Management of sentinel surveillance sites
- Distribution of feedback materials, etc.
- Sentinel surveillance institution
- Report the total number of patients treated and the number of influenza-like illness patients to the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- Receipt of reporting data Feedback of analysis data
- Feedback of analysis data Report
Outbreak criteria
- 2024-2025 influenza season outbreak criteria ⌜8.6 cases per 1,000 outpatient visits
- Before the start of each season (September to the following August), expert advisory meetings will be held to establish outbreak criteria, and an influenza outbreak warning will be issued if the criteria are exceeded. * During an outbreak warning period, antiviral medications are prescribed based on suspected symptoms alone for high-risk groups for influenza (children, pregnant women or mothers within 2 weeks of childbirth, individuals over 65 years old, immunocompromised individuals, and those with underlying conditions) without separate testing, with health insurance coverage applied.
Incidence rate of influenza-like illness patients by solar term (solar term No. 19-20 to solar term No. 24-25)
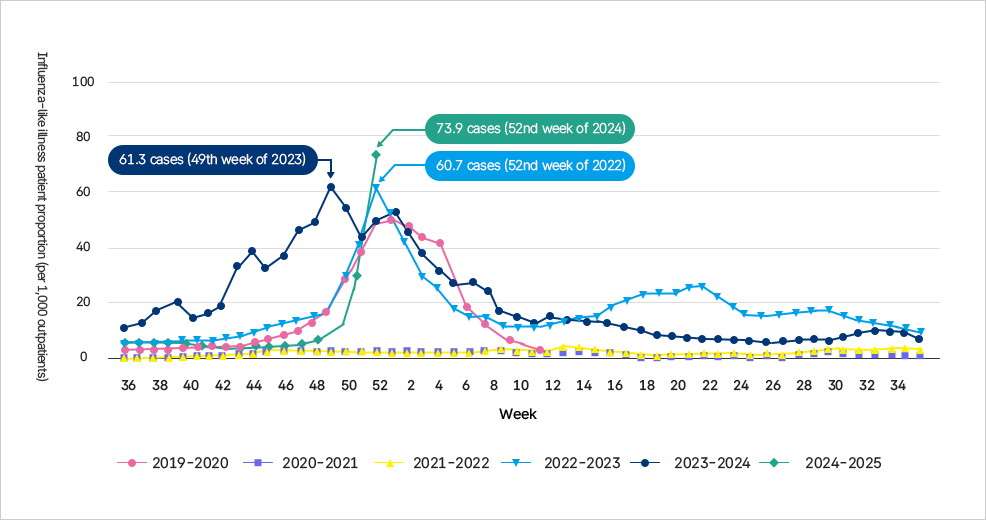
이 그래프는 2019-2020절기부터 2024-2025절기까지 인플루엔자 의사환자의 주차별 발생분율(인구 1,000명당 추정 환자 수)을 나타낸다. - 2019-2020절기와 2020-2021절기, 2021-2022절기에는 발생률이 낮거나 거의 없는 양상을 보였다. - 2022-2023절기에는 49주차에 약 61.3명, 52주차에 약 60.7명으로 환자 수가 급증한 후 빠르게 감소하였다. - 2023-2024절기에는 52주차에 73.9명으로 가장 높은 발생률을 기록했으며 이후 감소하였다. - 2024-2025절기는 현재까지 상대적으로 낮은 수준을 유지하고 있으며, 14~22주차 구간에서 다른 절기와 달리 완만한 증가 추세가 관찰된다. 그래프 전체적으로 최근 절기일수록 환자 발생 정점이 뚜렷하게 형성되고 있으며, 겨울철(49~2주차)에 집중적으로 발생하는 특징이 나타난다.
Monitoring of Influenza-related Hospitalizations and Deaths
Definition of reporting criteria terminology
- Total influenza patients
- New hospitalized patients, outpatients, and emergency room visits diagnosed with influenza
- Influenza outpatients
- New outpatients and emergency room patients diagnosed with influenza
- Influenza-related deaths
- Among the death cases at sentinel surveillance sites, those who received a confirmed influenza diagnosis within 30 days before death
Objective
- Monitor hospitalizations and deaths due to influenza each season to assess severity
Designation of sentinel surveillance sites
- Sentinel surveillance medical institutions for acute respiratory infections * Designation criteria: Public hospitals and medical institutions with 200 or more beds, and tertiary care hospitals
