Establishment and Operation of a National Wastewater-based Infectious Disease Monitoring System
Overview
- In addition to the existing patient-hospital-centered infectious disease monitoring system, a "national wastewater-based infectious disease monitoring system" has been established and is currently in operation since 2023 to efficiently track the trends of infectious disease outbreaks.
Project Details
- The concentration of infectious disease pathogens in domestic wastewater from nationwide monitoring points is periodically measured and analyzed to understand the trends of infectious disease outbreaks in the community, complementing the existing patient-hospital-based infectious disease monitoring system..
Table 1-69 | Pathogens Monitored in Wastewater
| Year | Monitoring Points (Public Wastewater Treatment Plants) |
Monitoring Rate (%) | Pathogens Under Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 63 locations | 52.7 | (3 types) COVID-19 virus, human influenza virus, norovirus |
| 2024 | 84 locations | 62.4 | (4 types) COVID-19 virus, human influenza virus, norovirus, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) |
Implementation Results
Detection of Pathogen Genes in Wastewater
- As of 2025, wastewater is sampled weekly from 99 sewage treatment plants nationwide to analyze coronavirus, human influenza virus, norovirus, and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). Wastewater surveillance results for coronavirus, influenza virus, and norovirus are disclosed through the Infectious Disease Portal
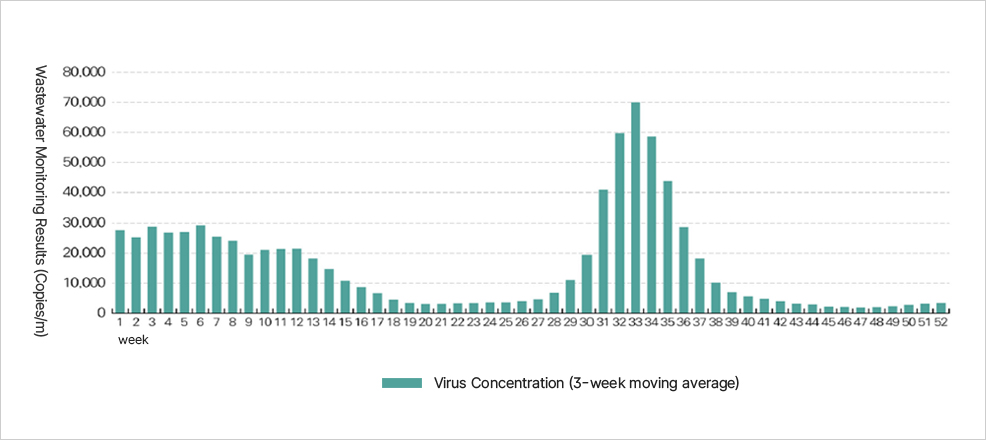
이 그래프는 하수 감시 결과를 통해 주차별 바이러스 농도의 변화를 나타낸다. 수치는 3주 이동평균을 기준으로 한 Copies/mL 단위이다.
- 1~10주차: 약 20,000~30,000 수준으로 비교적 높게 유지되다가 점차 감소한다.
- 11~20주차: 20,000 이하로 내려가며, 15주차 이후에는 10,000 이하로 크게 줄어든다.
- 21~30주차: 최저 수준을 유지하다가 30주차 이후 급격히 증가한다.
- 31~35주차: 70,000까지 치솟으며 최고점을 기록한다.
- 36주차 이후: 다시 급감하여 40주차에는 10,000 이하, 45주차 이후에는 5,000 이하로 안정화된다.
의미: 연중 대부분은 낮은 농도로 유지되지만, 30~34주차 사이에 바이러스 농도가 급격히 증가하여 감염 확산 위험이 집중되는 시기가 있음을 보여준다.
