HIV Transmission Rate
For the HIV virus pathogen to infect another person, it must meet both of the following conditions.
First, the amount of exposed virus must be sufficient to cause an infection.
The HIV virus is found in the blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk of infected patients, and exists in smaller amounts in pleural fluid and cerebrospinal fluid.
Second, the HIV virus must enter the bloodstream.
Infection occurs when the virus enters the body through the vaginal or rectal mucosa, directly into the bloodstream via a syringe needle, or when it penetrates the vascular system through broken skin such as wounds, eyes, nose, or the mucous membrane at the tip of the penis.
Routes of HIV Infection
- The main routes of HIV infection are through sexual contact (unsafe sexual contact with an infected person), transfusion of infected blood (when receiving blood or blood products contaminated with HIV), sharing of contaminated syringes (when using a syringe used by an infected person), and mother-to-child transmission (during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding from an infected woman).
- There is also a possibility of infection if exposure occurs during medical procedures performed by healthcare professionals. As of now, there have been no reported infections due to exposure among healthcare professionals in Korea.
| HIV infection routes | Content | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sexual contact | Transmission route HIV is transmitted when semen, vaginal fluids, or blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person during sexual activity. HIV is found in semen and cervical/vaginal secretions, and it is more likely to be transmitted when there are signs of inflammation due to sexually transmitted infections, ulcers in the genital mucosa, or injuries to the genitals. |
|||||||||||||
| Infection probability The probability of infection from a single sexual contact with an infected person is between 0.04% and 1.38%.
※ Source: HIV Risk Behaviors, 2015 CDC)
|
||||||||||||||
| Infection distribution The most significant transmission route worldwide. In Korea, it has been found that over 99% of all HIV-infected individuals were infected through sexual contact, indicating that sexual contact plays a significant role in the spread of HIV. Characteristics Anal intercourse is the riskiest sexual behavior, and sexual contact without using condoms can lead to sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. Even with condom use, some infections like syphilis and herpes can be transmitted through skin contact. |
||||||||||||||
| Transfusion of infected blood | Transmission route Infection occurs when a person receives a direct transfusion of blood infected with HIV or is administered serum produced from an infected person’s blood. The risk of HIV transmission is also high when transfusing blood products such as whole blood, concentrated red blood cells, platelets, white blood cells, and plasma. Infection probability The probability of infection from receiving a transfusion of infected blood is approximately 93%.
※ Source: HIV Risk Behaviors, 2015 CDC
|
|||||||||||||
| Infection distribution Recently, thorough infection screening (including HIV screening tests and nucleic acid amplification tests) has been conducted on blood used for transfusions, and since 2006, there have been no reported cases of infection from blood transfusions. |
||||||||||||||
| Characteristics Infection does not occur through gamma globulin, hepatitis B immunoglobulin, or plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccines. |
||||||||||||||
| Transmission route | Transmission route When a drug user abuses drugs through intravenous injection and shares their used syringe with others, HIV can be transmitted through the contaminated needle. Infection probability The probability of infection from shared use of a syringe needle is approximately 0.6%.
※ Source : HIV Risk Behaviors, 2015 CDC
|
|||||||||||||
| Infection distribution Five cases have been reported in Korea |
||||||||||||||
| Characteristics In Korea, it is possible to purchase syringes without a doctor’s prescription, and the number of drug users who use syringes is low, resulting in significantly lower transmission rates due to shared syringe use compared to other countries. |
||||||||||||||
| Mother-to-child transmission | Transmission route Infection can occur through the placenta during pregnancy or during the childbirth process. Infection through breastfeeding is also possible. Infection probability The probability of mother-to-child transmission is approximately 23% (although individual differences exist, the average infection rate with preventive measures is 2-10%).
※ Source : HIV Risk Behaviors, 2015 CDC
|
|||||||||||||
| Infection distribution In cases where infection is transmitted from an infected mother to the baby: Globally, 90% of HIV infections in newborns and children are mother-to-child transmissions. |
||||||||||||||
| Characteristics Transmission is more likely from a mother with AIDS symptoms or a high viral load in the blood, and a mother infected with HIV during pregnancy has a relatively high amount of the virus in the early stages of infection, making fetal infection easier. However, if the currently implemented chemical prophylaxis is followed, a healthy baby can be born. |
Statistics on HIV Transmission Routes in Korea
2023 Status of HIV/AIDS Reports in Korea: Epidemiological Survey on Routes of Transmission Statistics
| Category | Number of cases surveyed (individuals) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total sum | 566 | (100.0) |
| Sexual contact | Between opposite genders 258 |
(45.6) |
| Between same genders 306 |
(54.1) | |
| Mother-to-child transmission | 0 | (0.0) |
| Others | 2 | (0.4) |
The investigation of transmission routes was conducted based on responses from the infected individuals during the epidemiological survey at health centers, excluding non-responses.
1) Shared use of syringes, etc. (Source: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (2024). 2023 HIV/AIDS Notification Status Yearbook)
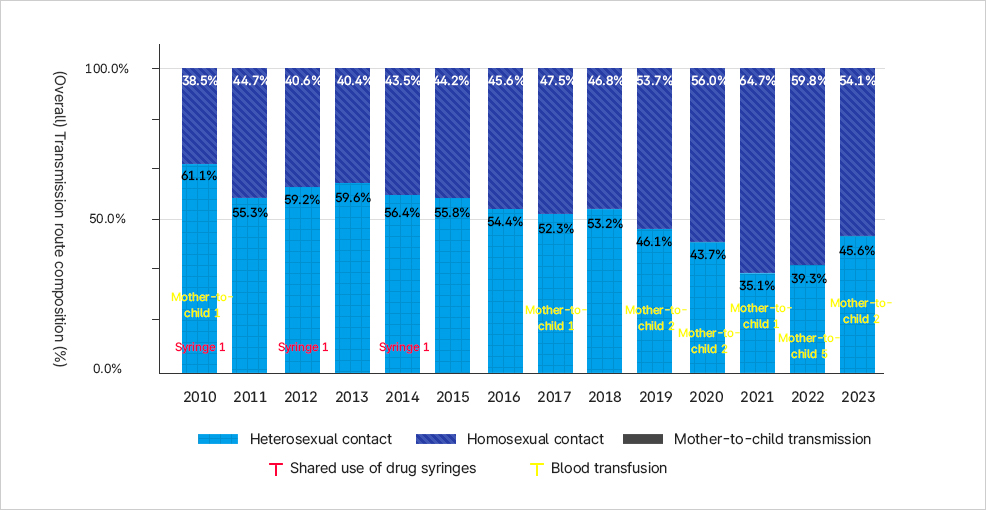
이 그래프는 2010년부터 2023년까지 국내 HIV/AIDS 신규 감염자의 전파 경로 구성을 백분율로 나타낸 누적 막대그래프다. 구성 요소는 이성 성접촉, 동성 성접촉, 수혈, 수직감염, 마약 주사기 공동사용이다. - 이성 성접촉: 2010년 61.1%에서 시작했으나 점차 감소하여 2021년 35.1%까지 낮아졌다. 이후 2023년에는 45.6%로 다소 반등했다. - 동성 성접촉: 2010년 38.5%에서 꾸준히 증가해 2021년에는 64.7%로 정점을 찍었으며, 2023년에도 54.1%로 절반 이상을 차지했다. - 수혈 및 수직감염: 2010년대 초반 일부 사례가 보고되었으나 전체 구성비에서 차지하는 비율은 극히 낮고, 최근에는 거의 나타나지 않았다. - 마약 주사기 공동사용: 2010년 이후 지속적으로 관찰되나 비율은 낮고, 주로 1~2% 수준을 유지했다. 전체적으로, 2010년 이후 전파 경로는 이성 성접촉 비중이 줄고 동성 성접촉 비중이 크게 증가하는 추세를 보이며, 수혈·수직감염·주사기 공동사용은 미미한 수준으로 나타난다.
[Korean HIV/AIDS Cohort Study] Transmission Routes of Study Participants
| Category | Survey participants | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total sum | 1,509 | 100.0 |
| Homosexual/Bisexual contact | 953 | 63.2 |
| Heterosexual contact | 5431) | 36.0 |
| Mother-to-child transmission | 0 | 0.0 |
| Blood transfusion | 4 | 0.4 |
| Blood coagulation factor product | 2 | 0.1 |
| Shared use of drug syringes | 1 | 0.1 |
| Others2) | 6 | 0.4 |
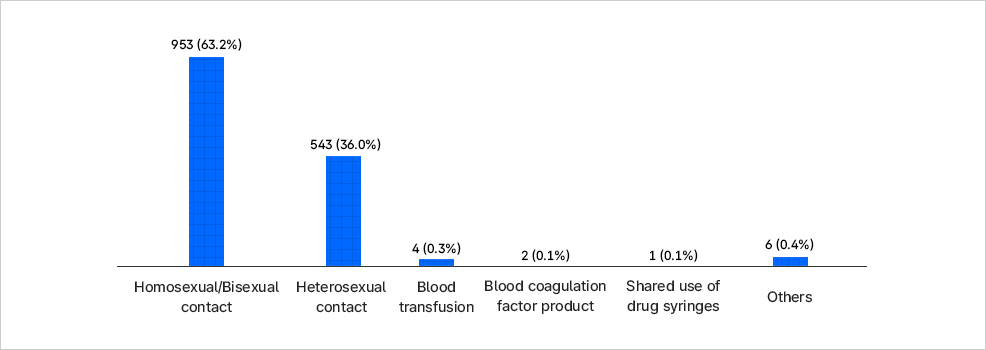
이 그래프는 HIV/AIDS 신규 감염자의 전파 경로별 분포를 막대그래프로 나타낸 것이다. - 동성/양성 간 성접촉: 953명, 전체의 63.2%로 가장 높은 비중을 차지한다. - 이성 간 성접촉: 543명, 36.0%로 두 번째로 많다. - 수혈: 4명, 0.3% - 혈액응고제제: 2명, 0.1% - 마약 주사기 공동사용: 1명, 0.1% - 기타: 6명, 0.4% 즉, 전체 감염자의 대부분은 성접촉(특히 동성/양성 간 성접촉)으로 인한 감염이며, 수혈·혈액응고제제·주사기 공동사용 등 다른 경로는 극히 적은 비중을 차지한다.
The data is based on responses from participants in the “Korean HIV/AIDS Cohort Study” from 2006 to 2021, excluding non-responses.- Includes one respondent who reported sexual contact.
- Infections due to acupuncture, tattoos, injection needles, etc.
